Selecting the Right Welding Helmet: A Complete Guide to Weld Shade Numbers and Visibility
To weld safely and effectively, selecting the right Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is non-negotiable. Among the most critical pieces of your welding PPE is the welding helmet. But not all welding helmets are the same, and the most crucial feature to understand is the lens shade number. Choosing the correct shade protects your eyes from harmful radiation and allows for the clear visibility needed to produce a quality weld. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about welding helmet shades, from deciphering a shade chart to understanding how modern auto-darkening helmets can revolutionize your welding experience. Let's make sure your next weld is both safe and precise.
Why is the Correct Shade Number Crucial for Any Weld?
The primary function of a welding helmet is to protect your eyes and face from the intense ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation emitted by the welding arc. This radiation is incredibly powerful and can cause severe and permanent eye damage in a matter of seconds. A condition commonly known as "arc eye" or "welder's flash" is an extremely painful inflammation of the cornea, and repeated exposure can lead to long-term vision problems. The correct shade number on your helmet's lens ensures that this harmful radiation is filtered out to a safe level, providing adequate protection for your eyes while you weld.
Beyond safety, the correct shade number is vital for achieving a high-quality weld. Visibility is key. If your lens shade is too dark, you won't be able to see the weld puddle, the joint, or your travel speed clearly. This can lead to poor bead placement, inconsistent welds, and defects. Conversely, if your shade is too light, the intense brightness of the arc will be overwhelming, causing you to squint and making it impossible to focus on the details of the weld. The right shade provides the perfect balance, allowing you to comfortably view your work, control the weld puddle, and produce strong, clean welds every single time. Your ability to see the weld directly impacts the quality of the weld.
What Exactly is a Welding Helmet Shade Number?
A welding helmet shade number is a rating that indicates how dark the lens of the helmet is and how much light it allows to pass through. The rating system, often based on a DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) standard, is simple: the higher the number, the darker the lens. For instance, a shade 3 or 4 is very light, suitable for grinding or setting up your weld, while a shade 14 is extremely dark, used for very high amperage arc welding applications. This number indicates the level of protection the filter offers against the brilliant light of the weld.
These shades are not arbitrary; they are precisely calibrated to filter out specific amounts of light and radiation. Most welding helmets come with a range of available shades, from approximately 5 to 14. Helmets can be categorized as either fixed shade, meaning they have a single, unchangeable shade number, or variable shade, which is common in modern auto-darkening welding helmets. A variable shade lens allows the welder to select the appropriate darkness for a specific welding task, offering much greater flexibility. Understanding what this number represents is the first step in selecting the right welding helmet for your protection.

Auto-Darkening vs. Fixed Shade: How Does it Affect Lens Shade Selection?
When you choose a welding helmet, one of the first decisions is between a fixed shade and an auto-darkening lens. A fixed shade helmet has a lens that is permanently set to a single shade number, usually a #10. These are simple, often less expensive, and reliable. However, the welder cannot see through the dark lens to set up the weld. This requires the classic "helmet nod"—positioning the electrode while the helmet is up and then nodding it down just before striking the arc. This can be inefficient and may lead to starting the weld in the wrong position.
In contrast, auto-darkening welding helmets have transformed welding practices for many professionals. These helmets have a special electronic filter with a light shade (typically #3 or #4), allowing for clear visibility before you start to weld. The moment arc sensors on the helmet detect the flash of the weld, the lens instantly darkens to a pre-selected shade number. This hands-free operation increases accuracy and efficiency, as you can set up your weld with the helmet already in position. This technology is a game-changer for any welder, especially when performing numerous tacks or working in tight spaces. The ability to see clearly before, during, and after the weld makes the entire welding process safer and more precise.
How Do You Use a Welding Helmet Shade Chart to Choose the Right Shade?
The most reliable tool for selecting the correct shade for any weld is the welding helmet shade chart. This essential guide, often provided by manufacturers and safety organizations like OSHA, correlates the welding process you are using with the amperage of your welding machine to recommend the appropriate shade level. The principle is straightforward: the more amperage you use, the brighter the arc, and the darker the shade you need to protect your eyes. A welder must learn to use this chart effectively.
To use the chart, you first identify your welding process—for example, Shielded Metal Arc Welding (Stick), Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG), or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (TIG). Then, find the amperage range you will be using for your specific weld task. The chart will then provide a recommended shade number or a small range of numbers. For example, for TIG welding between 50 and 150 amps, the chart might recommend a shade #10 or #11. It's a simple yet critical step to ensure you choose the right welding helmet shade every time you weld.
Example Welding Helmet Shade Chart
| Welding Process | Amperage (Amps) | Recommended Shade Number |
|---|---|---|
| Stick (SMAW) | 60 - 160 A | 10 - 11 |
| 160 - 250 A | 12 - 13 | |
| 250 - 550 A | 14 | |
| MIG (GMAW) | 60 - 160 A | 10 - 11 |
| 160 - 250 A | 11 - 12 | |
| 250 - 500 A | 13 - 14 | |
| TIG (GTAW) | 5 - 50 A | 8 - 9 |
| 50 - 150 A | 10 - 11 | |
| 150 - 500 A | 12 - 13 |
Note: This is a simplified guide. Always refer to the chart provided by your helmet manufacturer.
What Happens if My Weld Shade is Wrong?
Using the wrong shade number when you weld can have immediate and long-term consequences for both your health and the quality of your work. The risks are significant, which is why proper lens shade selection is a fundamental aspect of safe welding practices. You must protect your eyes from the intense light of the weld.
If you choose a shade that is too light for your weld, the arc will be uncomfortably bright. This immediate glare will cause you to squint, leading to eye strain, headaches, and fatigue. More seriously, a lighter shade than recommended may not provide adequate protection against UV and IR radiation, increasing your risk of arc eye. On the other hand, using a shade that is too dark will severely impair your visibility. You won't be able to see the weld joint, monitor the weld puddle, or control your travel speed and angle effectively. This lack of visibility while welding almost always results in a poor-quality weld, with defects like undercut, overlap, or an inconsistent bead profile. The wrong shade can cause eye strain and compromise the integrity of the weld.
Does the Type of Welding Process Change the Shade I Need?
Yes, absolutely. Different welding processes produce arcs of varying intensity, and therefore require different shade levels. Selecting a shade based on the type of welding you are performing is a critical step. A general-purpose shade might work for some applications, but for the best protection and visibility, you should match your welding helmet shade to the specific process.
For example, TIG welding often uses lower amperages and produces a less intense arc compared to other processes. This means you can typically use a lighter shade, which helps with the precision this type of welding demands. Stick welding and flux-cored arc welding, however, are known for producing a very bright and intense arc with lots of spatter, necessitating a much darker shade for proper eye protection. MIG welding falls somewhere in the middle. Even for specialized processes like plasma cutting or gas welding, there are specific shade recommendations. Always consult a shade chart to find the correct shade for the various welding processes you will be performing.
Are There Other Factors That Influence My Shade Choice?
While the welding process and amperage are the primary determinants for your shade number, a few other factors can influence your final decision. Personal comfort and vision play a significant role. Some welders may have more sensitive eyes and prefer a slightly darker shade than what the chart recommends, while others may opt for a lighter shade to get a clearer view of the weld puddle, as long as it's within a safe range.
The environment in which you weld also matters. If you are welding in a brightly lit workshop or outdoors in the sun, you might need a different shade setting compared to welding in a dimly lit area. The type of material and its thickness can also be a factor, as welding on reflective materials like aluminum or stainless steel can increase the overall brightness. An auto-darkening helmet is particularly useful in these situations, as it allows you to adjust the shade based on these subtle variables to achieve the perfect balance of protection and visibility for each unique weld task.

How Do Modern Welding Helmets Improve Visibility and Shade Control?
Modern welding helmets, particularly auto-darkening models, have come a long way in providing welders with superior control and clear visibility. These helmets are equipped with advanced features that allow you to fine-tune your view for any welding task. The most significant feature is variable shade control. Instead of being locked into one shade, a welder can adjust the shade settings, often via an external knob, to perfectly match their welding application. This means you can use the same helmet for low-amperage TIG welding and high-amperage stick welding with just a quick adjustment.
Beyond variable shade, many high-quality auto-darkening welding helmets offer adjustable sensitivity and delay controls. Sensitivity control allows you to set how much light it takes to trigger the lens to darken, which is useful when welding near other welders. Delay control lets you adjust how long the lens stays dark after the welding arc stops, protecting your eyes from the still-glowing weld puddle. Furthermore, improvements in lens technology have led to better optical clarity, giving you a truer color view of the weld, which can help in identifying heat changes and puddle consistency. These features combine to make welding safer, more comfortable, and more precise.
What Safety Standards Should My Quality Welding Helmet Meet?
When buying a welding helmet, safety is of utmost importance. To ensure a helmet provides reliable protection, it must meet recognized safety standards. For a procurement manager like Mark Thompson, verifying these certifications is a crucial part of the purchasing process. In the United States, the primary standard is ANSI Z87.1. A helmet marked with "Z87.1" has been tested for impact resistance and its lens has been verified to provide the advertised level of UV/IR protection, even in its light state.
In Europe, the CE EN 379 standard applies to auto-darkening welding filters, specifying requirements for optical quality, switching speed, and protection levels. As a manufacturer exporting globally, we ensure our welding helmets are rigorously tested to meet these international safety standards. Never purchase a welding helmet that does not clearly display its compliance with these standards. A certified helmet is your guarantee that the product will perform as expected when you weld, protecting you from serious injury.
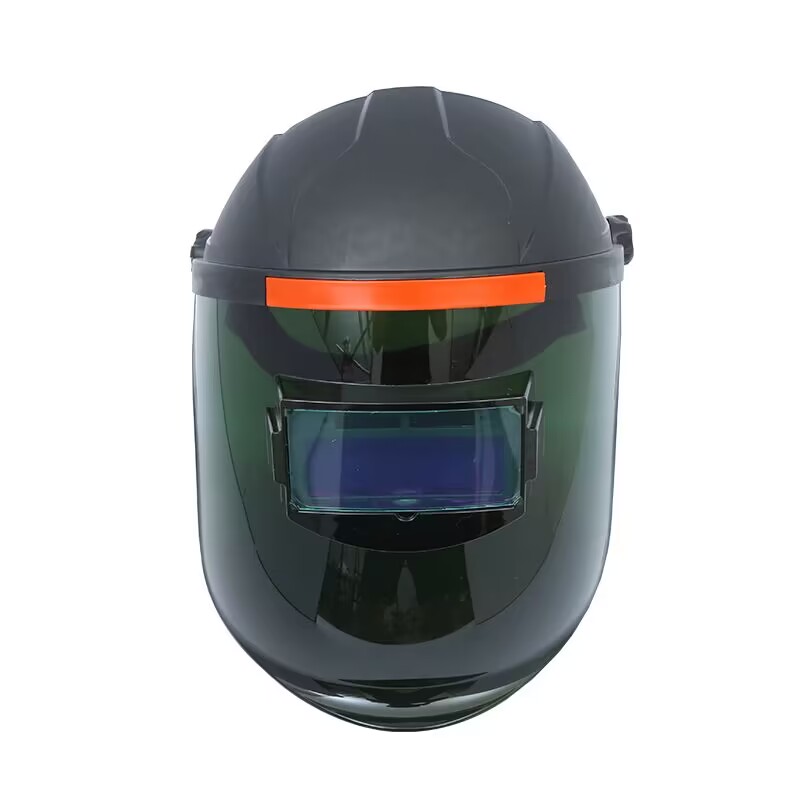

Putting It All Together: How Do I Choose the Right Welding Helmet for My Needs?
Selecting the right welding helmet is a personal decision that depends on your specific needs, the type of welding you do, and your budget. Start by deciding between a fixed shade and an auto-darkening helmet. For most welders, the convenience and enhanced visibility of an auto-darkening helmet make it a worthwhile investment. Next, consider the features you need. If you perform different welding processes, a helmet with a wide variable shade range is essential. For precision TIG work, look for a helmet with excellent low-amperage performance and multiple sensors.
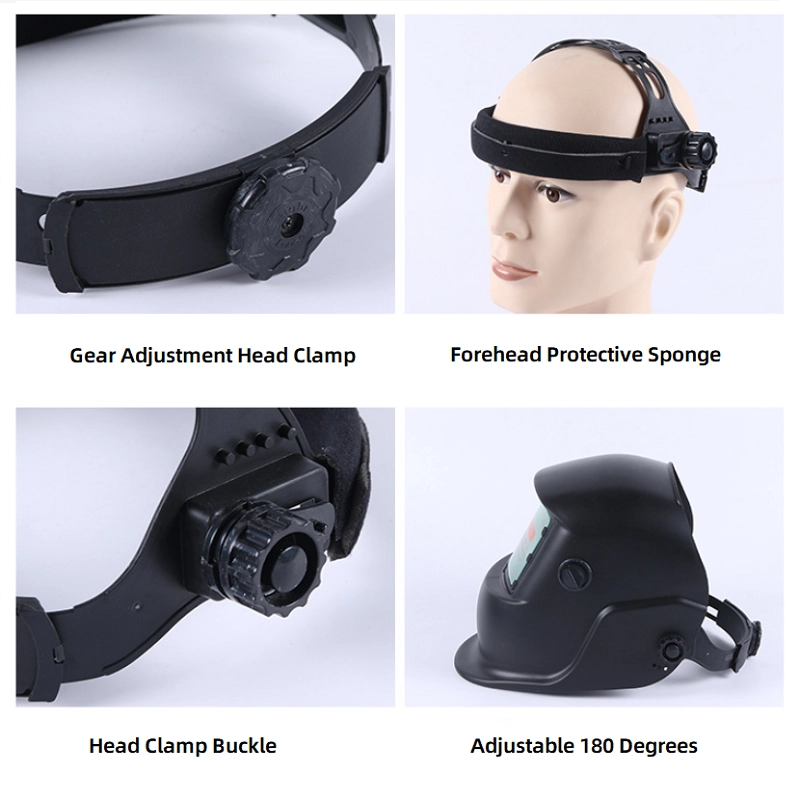
Don’t forget about comfort and ergonomics. The weight of the welding helmet and the design of the headgear are critical for comfort for extended use. A helmet may look great, but if it's uncomfortable, it will hinder your work. Look for a helmet with a large viewing area and high optical clarity for the best possible view of your weld. Finally, always verify that the helmet for your needs meets the required safety standards. By considering these factors—function, features, comfort, and safety—you can confidently choose the right welding helmet to protect your eyes and improve your weld quality.
Key Takeaways for Selecting the Right Weld Helmet Shade:
- Safety First: The primary purpose of the shade is to protect your eyes from harmful UV/IR radiation from the weld. Never weld without proper eye protection.
- Use a Shade Chart: Always refer to a welding helmet shade chart to match the correct shade number to your specific welding process and amperage.
- Balance Protection and Visibility: The goal is to choose a shade that is dark enough to protect you but light enough to allow a clear view of the weld puddle.
- Auto-Darkening Offers Versatility: Auto-darkening welding helmets provide superior convenience and flexibility, allowing you to adjust the shade for different welding tasks.
- Consider Your Process: The type of welding you are doing (TIG, MIG, Stick) is a primary factor in determining the shade you need.
- Check for Standards: Ensure any welding helmet you purchase is certified to meet safety standards like ANSI Z87.1 or CE EN 379.