Mastering the Arc: Your Definitive Guide to Welding Electrodes and Manual Electrode Holders for Superior Welds
Hello Mark, and to all procurement officers and business owners in the safety equipment and welding supply industry! As Allen, with years of experience in manufacturing and supplying top-quality protective gear from China, I understand your need for reliable, durable, and cost-effective solutions. This article is designed to give you a clear, practical understanding of welding electrodes and manual electrode holders. We'll explore how selecting the right components is crucial not just for achieving a perfect weld, but also for ensuring the safety and efficiency of every welding and cutting operation. Whether it's for arc welding, spot welding, or general fabrication, knowing your electrode and electrode holder inside out is key. This guide will help you safely handle these essential tools and make informed purchasing decisions. You'll learn why a good electrode holder must be able to safely manage current and why it's designed for arc welding specifically.
What Exactly is a Welding Electrode and Why is it Fundamental to a Good Weld?
A welding electrode is the heart of many arc welding processes, particularly Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), often called stick welding. Think of it as a metal wire, often called a welding rod, that is coated with special chemical compounds. This isn't just any wire, though. Its primary job is to conduct electricity from the welding power source (your welding machine) to the workpiece. As the electrode tip touches the metal you're working on, it creates an electric arc. This arc is incredibly hot – hot enough to melt both the electrode itself and the base metal.
The molten metal from the electrode (filler metal) mixes with the molten base metal, and as it cools, it forms the weld – the strong joint you're aiming for. So, you see, the electrode isn't just a conductor; it actively becomes part of the weld. The quality, strength, and characteristics of your final weld are directly influenced by the type of electrode you use. Using the wrong electrode can lead to a weak weld, cracks, or other defects, which can be costly and dangerous. For every welding project, the correct electrode is non-negotiable for a successful outcome.
The composition of the core wire of the electrode is chosen to be compatible with the metal being welded (e.g., mild steel, stainless steel, cast iron). When it melts, it adds material to the weld pool, filling the gap or groove between the two pieces of metal being joined. This ensures the weld has sufficient material to provide the required tensile strength and structural integrity. Therefore, understanding the function of the electrode is the first step towards achieving high-quality welding results.

Mark, selecting the correct electrode is a critical decision that directly impacts the quality and integrity of the weld. It's not a one-size-fits-all situation. Several factors to consider include the type of base metal, the thickness of the material, the required tensile strength of the weld, the welding positions you'll be working in (flat, horizontal, vertical, overhead), and the type of welding current (AC or DC) your welding machine supplies. For instance, welding thick steel plates will require an electrode different from one used for thin sheet metal.
The diameter of the electrode is another crucial factor. Thicker materials generally require larger diameter electrodes and higher welding current, while thinner materials need smaller diameter electrodes to prevent burn-through. The electrode selection process also involves considering the desired properties of the finished weld, such as corrosion resistance or ductility. Each electrode is designed for specific applications, and its coating (which we'll discuss next) plays a huge role in its performance characteristics. As a supplier, ensuring your customers have access to a good range of welding electrodes and the knowledge to choose the correct electrode is paramount for their success and safety.
Ultimately, choosing an electrode that matches the base material and meets the requirements of the welding job is key. An improperly chosen electrode can lead to a host of problems, including poor penetration, excessive spatter, porosity in the weld, or even cracking. This is why manufacturers like us provide detailed specifications for each electrode, often following AWS (American Welding Society) classifications, to guide the welder in making the right choice for their specific welding operation.
The Unsung Hero: What is the Role of the Electrode Coating in the Welding Process?
The coating on a welding electrode is far more than just a protective layer for the core wire; it's a sophisticated mix of minerals, metals, and binders that performs several vital functions during the arc welding process. When the arc is struck, the coating on the electrode decomposes under the intense heat. This decomposition releases gases that form a protective shield around the molten weld pool. This shield displaces atmospheric oxygen and nitrogen, which, if allowed to enter the molten weld, would cause brittleness and porosity, significantly weakening the weld.
Furthermore, the coating contains "fluxing" agents. These agents help to clean and deoxidize the molten weld metal, removing impurities and resulting in a cleaner, stronger weld. As the weld cools, some components of the coating solidify on top of the weld bead, forming a layer called slag. This slag layer protects the hot weld metal from atmospheric contamination as it cools and also helps to shape the weld bead. Once the weld is cool, the slag is typically chipped or brushed away. The type of coating also influences the arc stability, penetration depth, deposition rate, and the mechanical properties of the finished weld. Different coatings are designed for different welding positions and types of welding current, making the electrode incredibly versatile.
The composition of the electrode coating can also add alloying elements to the weld metal, enhancing its properties like tensile strength, hardness, or corrosion resistance. This is particularly important when welding alloy steels or when specific mechanical properties are required for the weld. Therefore, understanding the role of the coating is essential when choosing the right electrode for a particular welding job. It’s this complex chemistry that allows a simple-looking welding rod to produce a strong and reliable weld.
Decoding the Labels: What Do AWS Electrode Classifications Tell You About a Welding Rod?
Mark, when you look at a package of welding electrodes, you'll see a series of letters and numbers, like E6013 or E7018. This isn't just random jargon; it's the AWS (American Welding Society) classification system, a standardized code that tells you a lot about the electrode and its intended use. Understanding this system is crucial for electrode selection and ensuring the weld meets specific requirements. Let’s take E7018 as an example for a low hydrogen electrode.
- E: This stands for electrode, indicating it's used for arc welding.
- First two (or three) digits (e.g., 70): This indicates the minimum tensile strength of the deposited weld metal, in thousands of pounds per square inch (psi). So, E70xx means the weld will have a minimum tensile strength of 70,000 psi. This is a key factor for structural applications where the weld must bear significant loads.
- Third digit (e.g., 1 in E7018): This number indicates the welding positions in which the electrode can be used. '1' means it's an all-position electrode (flat, horizontal, vertical, and overhead). '2' would mean flat and horizontal positions only.
- Fourth digit (e.g., 8 in E7018): This digit provides information about the type of coating, the type of welding current (AC, DC positive, DC negative), and the penetration characteristics of the electrode. For instance, an '8' here signifies a low hydrogen electrode coating, typically requiring DC positive current, known for producing high-quality, crack-resistant welds.
This classification system provides a concise way for welders and procurement specialists like yourself to identify and select the correct electrode for a specific type of welding application without ambiguity. It ensures consistency and reliability in welding operations across different manufacturers and projects. Knowing these codes helps in matching the electrode to the base material, the welding machine capabilities, and the structural requirements of the welding task.
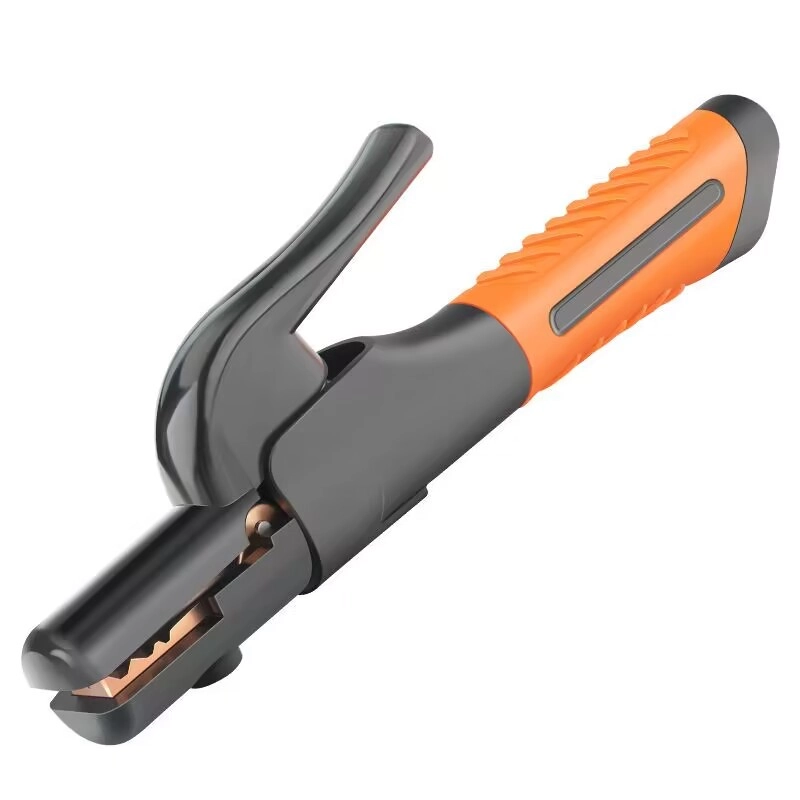

Beyond Just Holding: What Makes a Manual Electrode Holder So Vital for Welder Safety and Control?
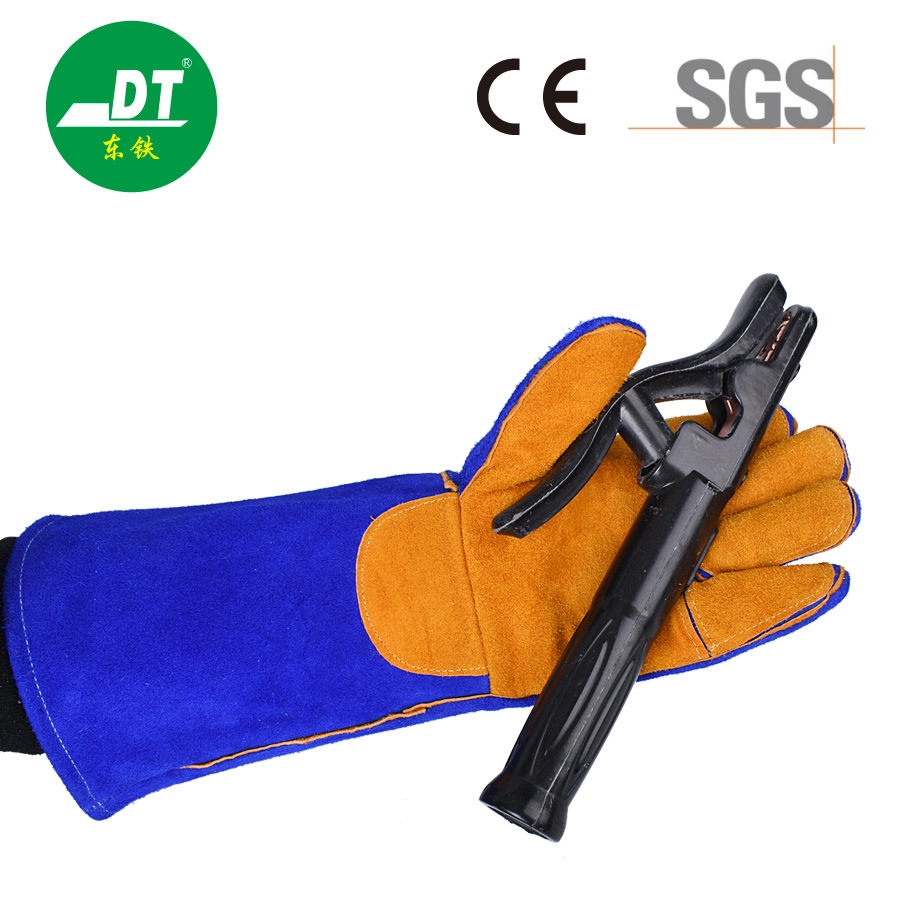
While the electrode does the work of creating the weld, the manual electrode holder (often simply called an electrode holder or stinger) is the welder's direct interface with the live electrical circuit. Its importance cannot be overstated. A well-designed electrode holder allows the welder to securely grip and manipulate the electrode during the welding process. It must provide excellent electrical contact with the electrode to ensure a stable arc and efficient transfer of the welding current. If the connection is poor, it can lead to arc instability, inconsistent weld quality, and even cause the electrode holder to overheat.
Crucially, the electrode holder is a primary safety device. It must be able to safely conduct the welding current without overheating and must be fully insulated against the maximum voltage of the welding power source. This insulation protects the welder from accidental electric shock, which is one of the significant hazards associated with arc welding and cutting. The design should ensure that the welder cannot make electrical contact with any live parts when gripping the holder or changing the electrode. A high-quality electrode holder will have robust insulation on the handle and jaws.
Moreover, the ergonomic design of an electrode holder contributes to welder comfort and control, reducing fatigue during long welding sessions. This, in turn, can lead to better weld quality and increased productivity. The jaws of the electrode holder must securely grip various diameter electrodes at different angles, allowing the welder flexibility in various welding positions. Investing in a good electrode holder is investing in safety, efficiency, and the quality of the weld. From my experience supplying welding equipment, a reliable electrode holder like our Dongtie 500A 800A Electrode Holder is a non-negotiable part of a professional's toolkit.
Choosing Wisely: What Factors Should Guide Your Selection of a Welding Electrode Holder?
Mark, when you're looking to procure welding electrode holders for your clients or your own operations, several key factors come into play. The first and foremost is the amperage rating. The electrode holder must be capable of safely handling the maximum rated current that will be used for the welding operation. Using an undersized electrode holder for the current required can cause it to overheat, leading to damage to the holder, poor weld quality, and significant safety risks for the welder. Always match the holder's amperage rating to the output of the welding machine and the requirements of the electrode being used.
The duty cycle of the electrode holder is another important consideration, especially for industrial applications. Duty cycle refers to the percentage of a 10-minute period that the holder can operate at its rated current without overheating. For heavy-duty, continuous welding, a holder with a higher duty cycle is essential. Also, consider the range of electrode diameters the electrode holder can accommodate. Most holders come with jaws designed to grip various common sizes, but it's good to verify this matches the types of electrodes your welders will be using.
Comfort and ergonomics are also vital. A well-balanced electrode holder with a comfortable, non-slip grip reduces welder fatigue and improves control, especially during extended use. The ease of inserting and releasing the electrode also impacts efficiency. Finally, durability is key. Look for welding electrode holders made from high-quality, heat-resistant materials with strong, well-insulated jaws and handles. These will withstand the rigors of the welding environment and provide a longer service life, offering better value in the long run. We design our electrode holders with these factors in mind, ensuring they meet stringent safety standards.

Safety First! What Key Features Insulate and Protect in Welding Electrode Holders?
Safety is paramount in any welding operation, and the electrode holder plays a critical role in protecting the welder. The most important safety feature is its ability to insulate the welder from the electric current. The handle and the body of the electrode holder must be made from high-quality, non-conductive, heat-resistant materials. This ensures that even if the welder is working in damp conditions or if their gloves are slightly worn, they are protected from electric shock. The electrode holder must be fully insulated against the maximum open-circuit voltage of the welding power source.
The design of the jaws is also crucial for safety. They should securely grip the electrode to prevent it from slipping, which could cause an erratic arc or accidental contact. Modern electrode holders often feature deeply grooved jaws that can hold the electrode at various angles, providing flexibility while maintaining a secure grip. Furthermore, the insulation should extend as close as possible to the tip of the jaws to minimize any exposed live parts when an electrode is clamped. This reduces the risk of accidental arcing if the holder touches the workpiece or a grounded surface.
Another safety aspect is the heat resistance of the materials used. During welding, the electrode holder can become quite hot due to the welding current passing through it and radiant heat from the arc. The insulating materials must withstand these temperatures without degrading, melting, or becoming conductive. This ensures safety throughout the welding process. When selecting an electrode holder, always check for compliance with relevant safety standards (like CE or ANSI requirements), which indicates it has been tested for these critical safety features. Protecting the welder's hands is also crucial, which is why pairing a good electrode holder with high-quality welding gloves is essential.
Why are Low Hydrogen Electrodes Preferred for Critical Welding Tasks?
Mark, when it comes to welding high-strength steels, thick sections, or materials prone to cracking, low hydrogen electrodes (like the E7018 we discussed earlier) are often the go-to choice. The "low hydrogen" designation means that the coating of these electrodes is specially formulated to contain minimal amounts of hydrogen-bearing compounds. Hydrogen is a major concern in welding because it can dissolve into the molten weld metal and, as the weld cools, can lead to a defect called hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) or delayed cracking. This type of cracking can occur hours or even days after the weld is completed and can severely compromise the integrity of the welded structure.
The coating on a low hydrogen electrode is designed to produce a weld deposit with very low levels of diffusible hydrogen. This makes them ideal for applications where the weld quality is critical and the risk of cracking must be minimized, such as in pressure vessels, bridges, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery fabrication. These electrodes typically produce a strong, ductile weld with excellent impact properties, even at low temperatures. This makes the resulting weld more resilient and reliable under demanding service conditions.
Using low hydrogen electrodes does come with specific storage and handling requirements. Because their coatings are hygroscopic (meaning they absorb moisture from the air), these electrodes must be stored in hermetically sealed containers or in heated ovens to keep them dry. If a low hydrogen electrode absorbs moisture, its low-hydrogen characteristics can be compromised, increasing the risk of weld defects. Proper handling and re-baking procedures, if they get damp, are crucial to maintain their performance and ensure a high-quality, crack-free weld. This attention to detail is why they are reserved for applications where the integrity of the weld is absolutely paramount.
Maximizing Lifespan and Performance: Why is Proper Maintenance of Electrodes and Holders Crucial?
Proper maintenance of both welding electrodes and electrode holders is essential not only for ensuring their longevity but also for maintaining weld quality and welder safety. For welding electrodes, especially low hydrogen electrodes, storage is key. As mentioned, they must be kept dry. Storing them in a warm, dry place, preferably in their original sealed packaging or a heated electrode oven, prevents moisture absorption which can lead to porosity and hydrogen embrittlement in the weld. Damaged or chipped coating on an electrode can also affect arc stability and shielding, so electrodes should be handled with care.
For electrode holders, regular inspection and maintenance are vital. Check the insulation on the handle and jaws for any cracks, chips, or burns. Damaged insulation can expose the welder to potential hazards like electric shock and must be repaired or the electrode holder replaced immediately. The jaws should be kept clean from spatter and oxidation to ensure good electrical contact with the electrode. A poor connection can cause the holder to overheat and lead to an unstable arc. The spring mechanism that clamps the electrode should also be checked for proper tension; if it's too loose, the electrode may not be held securely.
Cables connected to the electrode holder should also be inspected for wear and tear, cuts, or frayed wires, as these can pose serious safety risks. Ensuring a tight, secure connection between the cable and the electrode holder is also important to prevent overheating and voltage drops. By implementing a routine inspection and maintenance schedule for your welding equipment, including electrodes and manual electrode holders, you can significantly reduce the risk of equipment failure, improve weld quality, enhance safety, and extend the service life of your tools, ultimately saving costs and improving productivity. This proactive approach is something we always advocate for in the welding and cutting industry.

From My Factory to Your Floor: Ensuring Quality in Every Electrode and Holder
Mark, as a manufacturer specializing in protective gloves and apparel, including items essential for welders like durable cowhide welding aprons and flame retardant welding caps, I understand the critical importance of quality control. While we may not produce the welding electrode or electrode holder itself, the principles of ensuring high-quality, safe, and reliable products are universal. For businesses like yours that supply these crucial welding components, partnering with manufacturers who prioritize quality is paramount. This ensures that the electrode performs as specified by its AWS classification, delivering the expected tensile strength and weld characteristics.
When it comes to the welding electrode, quality control involves precise formulation of the core wire and the coating, consistent diameter electrodes, and rigorous testing to verify performance. This ensures each electrode will produce a reliable weld when used with the correct welding current and technique. Similarly, for an electrode holder, quality means robust construction using high-grade, insulate materials, secure jaw mechanisms, and designs that meet or exceed safety standards. The electrode holder must be designed for arc welding abuse, capable of safely handling the maximum rated current without failure.
Ultimately, high-quality electrodes and electrode holders contribute directly to better weld quality, increased productivity, and, most importantly, enhanced welder safety. Fewer weld defects mean less rework, saving time and materials. A comfortable, reliable electrode holder reduces fatigue and allows for more precise control. As someone who supplies equipment to professionals, you know that investing in quality upfront translates to long-term value and customer satisfaction. It's about providing tools that professionals can trust to perform their welding job safely and effectively, every single time, ensuring every weld is a testament to their skill and the quality of their welding equipment.
Key Takeaways to Remember:
Mark, I trust this detailed overview has been insightful. Here’s a quick recap of the most important points regarding welding electrodes and electrode holders:
- Electrode Selection is Crucial: Always choose the correct electrode based on base metal, thickness, welding positions, required tensile strength, and welding current (AC or DC). The AWS classification is your guide.
- Coating Matters: The electrode coating provides shielding gases, fluxing agents, slag protection, and can add alloying elements to the weld.
- Electrode Holder Safety: The primary role of an electrode holder is to safely handle the welding current and insulate the welder. Ensure it's rated for the amperage and fully insulated against the maximum voltage.
- Low Hydrogen Electrodes for Critical Welds: Use low hydrogen electrodes (e.g., E7018) for high-strength, crack-sensitive applications, and ensure proper storage to maintain their low-hydrogen properties.
- Quality Pays: Investing in high-quality electrodes and welding electrode holders leads to better weld quality, increased productivity, and enhanced welder safety.
- Maintenance is Key: Regular inspection and maintenance of both electrodes (especially storage) and electrode holders (insulation, jaws, cables) are vital for performance and safety.
- Understand the Tool: Both the electrode and the electrode holder are more than just simple tools; they are integral components of the arc welding system that directly influence the outcome of your welding project.
By keeping these points in mind, you can better serve your customers and ensure that the welders using your products are equipped for success and safety in every weld they create. If you have any further questions or need to discuss your specific needs for protective equipment, please don't hesitate to reach out.