Essential Welding Tools and Accessories Every Welder Needs to Enhance Safety and Efficiency
Welding is a craft that blends art with intense industrial power. Whether you are a seasoned professional or just starting, the difference between a clean, strong joint and a messy failure often comes down to the gear you use. But it is not just about the quality of the bead; it is about making sure you go home safe every night. This article explores the essential welding tools and safety gear that define a productive workshop. We will dive into why specific equipment matters, how to choose the right welding gear for your needs, and how these items enhance safety and performance. From the best welding helmets to the most durable gloves, we cover what every welder needs to master their trade with safety and efficiency.
Why Is a High-Quality Auto-Darkening Welding Helmet the First Defense?
When you strike an arc, things get bright—dangerously bright. The most iconic piece of safety equipment in the welding industry is the welding helmet. However, not all helmets are created equal. In the past, a welder had to nod their head to flip the visor down right before the weld started. This repetitive motion can strain the neck and often leads to a wandering hand, causing the welding arc to strike off-target.
Today, auto-darkening welding helmets are the standard for efficiency and safety. These helmets have sensors that detect the bright light of the arc welding process and darken the lens in a fraction of a millisecond. This allows the welder to see their workpiece clearly before the weld begins, ensuring precise placement of the electrode or wire. Once the welding arc stops, the lens lightens automatically. This seamless transition reduces eye strain and eliminates the need to constantly lift the helmet.
Furthermore, a good welding helmet protects against UV and IR radiation, which can cause permanent eye damage known as "arc eye." It also shields the face from flying sparks and hot spatter. When selecting a helmet, look for adjustable sensitivity and delay settings. These features allow you to customize the lens response based on the type of welding you are doing, be it MIG welding, TIG welding, or high-amperage stick welding.
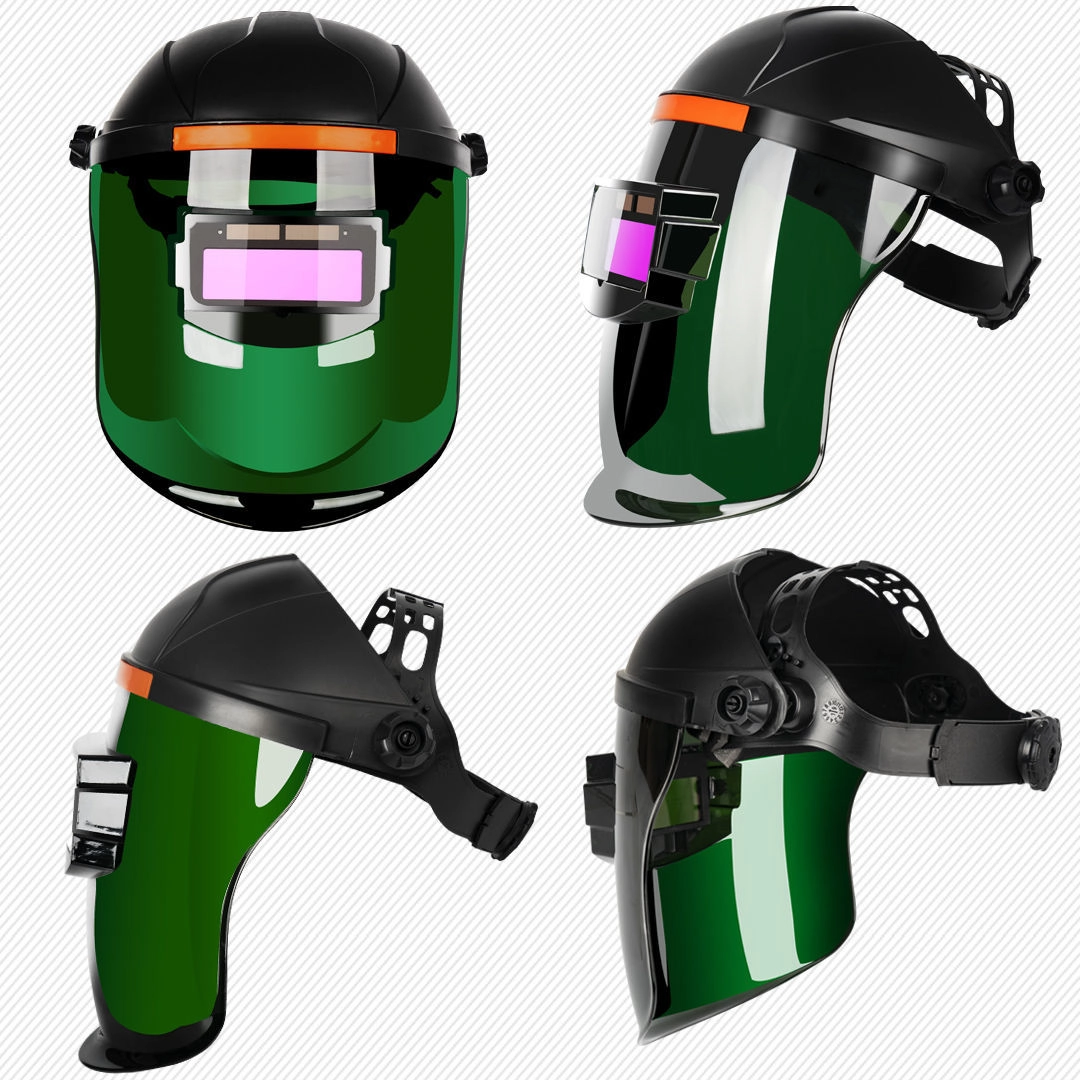

How Do You Select the Right Welding Gloves for Different Processes?
As a manufacturer in Shandong, I see thousands of gloves leave our factory, and I know that hands are a welder's most valuable tools. Welding gloves are not one-size-fits-all. The welding process generates intense heat, UV radiation, and spatter, so your hands need heavy-duty protection. However, the right welding glove depends entirely on the task at hand.
For heavy-duty welding like Stick or high-amperage MIG, you need thick, insulated gloves. These are usually made from cowhide or split leather. They provide excellent heat resistance but offer less dexterity. On the other hand, TIG welding requires a delicate touch to feed the filler rod. For this, goatskin or kidskin gloves are preferred because they are thinner and allow for greater movement, even though they offer less heat insulation.

Durability is key. A cheap glove might save money upfront, but if the seams burst or the liner unravels after a few welding sessions, it costs you productivity. Look for gloves with Kevlar stitching, which resists burning. Also, consider the lining. Cotton or fleece linings absorb sweat and add a layer of heat protection. We often recommend 14-inch thick palm welding protective gloves for heavy industrial work where heat is the primary enemy.
What Protective Clothing Is Necessary to Prevent Burns and UV Damage?
Sparks fly. It is an unavoidable part of the job. If you are wearing synthetic fabrics like polyester, those sparks will melt right through to your skin. Every welder needs dedicated welding clothing made from flame-resistant materials. A welding jacket is standard issue. These are typically made from leather, flame-retardant cotton, or a hybrid of both. Leather offers the best protection against heavy spatter, while cotton is lighter and more breathable for lighter work.
Don't forget the rest of your body. A leather apron acts as a shield for your torso and upper legs, which is critical when you are standing at a workbench. For your arms, welding sleeves can provide extra protection if you are wearing a lighter shirt.
Welding boots are another piece of essential safety gear. Dropping a heavy piece of steel or a hot electrode on your foot can end your career. Steel-toed boots with metatarsal guards are recommended. Additionally, make sure your pants cover the tops of your boots so sparks don’t fall inside. We produce heat and flame resistant cowhide welding work aprons that are designed to withstand the rigors of daily use in harsh environments.
Why Are Fume Extraction and Respiratory Safety Often Overlooked?
When metal melts, it releases fumes. Depending on what you are welding, these fumes can be toxic. Hazards associated with welding galvanized steel, for example, include "metal fume fever," caused by inhaling zinc oxide. Stainless steel can release hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen. Fume extraction is not just a luxury; it is a safety measure that protects your long-term health.
Many workshops use large ventilation systems, but personal respiratory protection is also vital. A respirator designed to filter out metal particulates fits under most welding helmets. For tighter spaces or more hazardous materials, a Powered Air Purifying Respirator (PAPR) system pumps clean air into your helmet, keeping the fume out and a cool breeze on your face.
Safety practices dictate that you should always position your head out of the fume plume. However, airflow in the welding area is tricky—you want enough ventilation to remove gas, but not so much draft that it blows away your shielding gas, which would ruin the weld. Balancing safety and efficiency here is key.
What Are the Essential Hand Tools Every Welder Needs in Their Arsenal?
You cannot shape metal with just a welding machine. A collection of essential welding tools helps you prepare, clean, and finish your work. First on the list are welding pliers. These specialized tools are the "Swiss Army Knife" for MIG welders. They are designed to trim wire, clean the gun nozzle, remove contact tips, and hammer away slag.
Another critical tool is the chipping hammer and wire brush. If you are doing stick welding or Flux-Core, you will have a layer of slag covering your weld bead. You need to chip and brush this away to inspect the quality of the joint. Even for cleaner processes like TIG, a stainless steel wire brush is needed to clean the metal before you start.
Welding clamps are vital. Metal moves when it gets hot. As the weld cools, it shrinks and pulls, which can warp your project. Heavy-duty C-clamps, locking pliers, and F-clamps hold your pieces firmly in place, ensuring the final geometry is correct. Without proper workholding, even the best welding technique won't save a project from being crooked.
- Essential Hand Tools Checklist:
- Welding Pliers (Nozzle cleaning, wire cutting)
- Wire Brush (Cleaning oxidation and slag)
- Chipping Hammer (Slag removal)
- Angle Grinder (Prep and finishing)
- Tape Measure (Precision layout)
How Do Welding Curtains and Screens Protect the Entire Workspace?
Welding safety isn't just for the person holding the torch; it is for everyone in the shop. The intense UV light from a welding arc can damage the eyes of anyone walking by, even from a distance. Welding curtains and screens are essential welding accessories that contain the hazard.
These screens are made from a transparent vinyl material that blocks harmful UV rays while allowing light to pass through, so the welder doesn't feel closed in. They also act as a barrier against flying sparks and grinding dust. By setting up a perimeter with screens, you define the welding area and alert others to the risks associated with welding taking place inside.
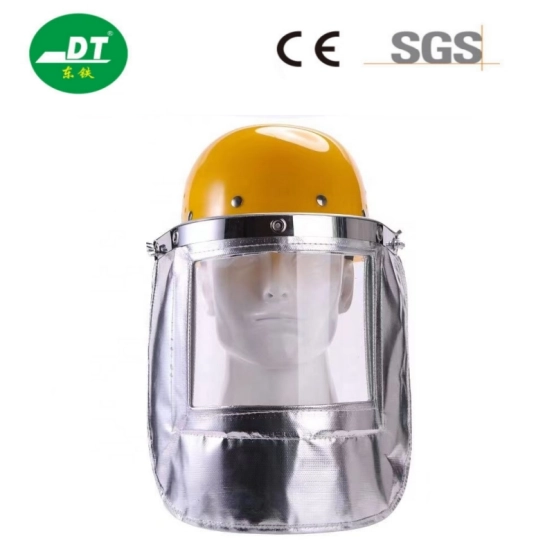

For high-heat environments, specific face screens are also used. For instance, an aluminum foil welding protective face screen reflects radiant heat, keeping the welder cool during long, high-amperage passes.
Why Are Quality Consumables like Electrodes and Wire Critical?
The welding machine provides the power, but the consumable provides the metal. Whether it is a stick electrode, a spool of MIG wire, or a TIG filler rod, the quality of your filler metal determines the strength of the weld. Using old, rusty, or damp electrodes can lead to porosity, cracking, and weak joints.
Storage is an often-ignored aspect of welding. Low-hydrogen electrodes (like 7018) must be kept in an oven to prevent them from absorbing moisture from the air. Even MIG wire can rust if left out in a humid shop, which causes the wire to jam in the liner.
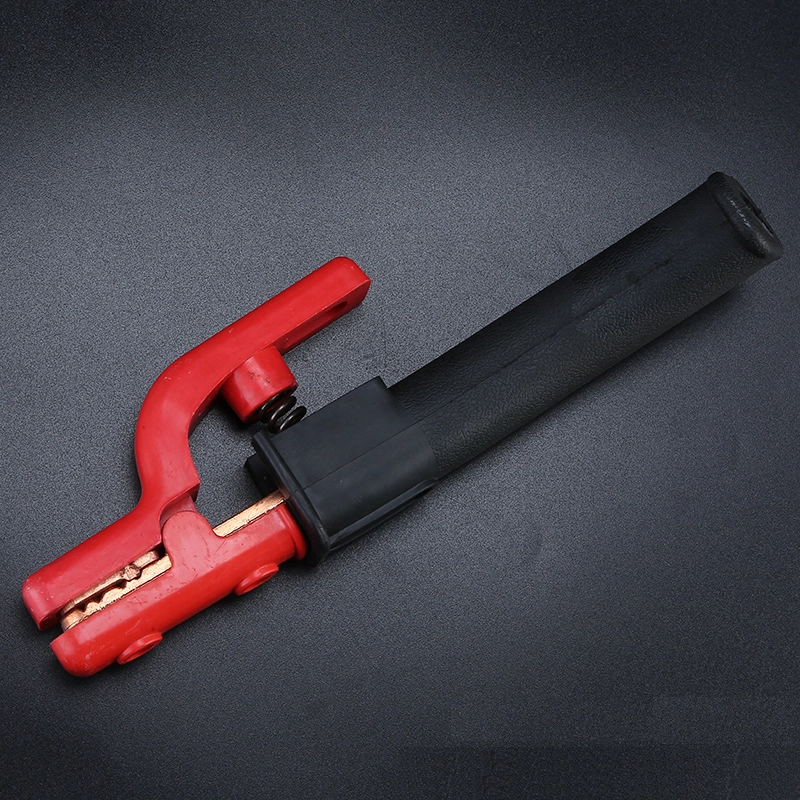
Additionally, the electrode holder itself matters. A loose or damaged holder can cause arcing, overheating, and inconsistent power delivery. A robust holder, such as a 800-1000A bending handle anti-drop electrode holder, ensures a secure grip on the rod and efficient current transfer, making the welding process smoother and safer.
How Does a Welding Cart and Table Improve Workflow?
A cluttered floor is a dangerous floor. Welding cables, gas hoses, and power cords are tripping hazards. A welding cart is a simple solution that organizes your welding machine, gas cylinder, and tools into one mobile unit. This allows you to bring the welding equipment to the work, rather than dragging the work to the machine.
Similarly, a good welding table is the foundation of accuracy. Metal tables allow you to clamp your workpiece down anywhere. Many tables have holes or slots for specialized fixtures. Furthermore, because the table is metal, it can serve as the grounding point for your work clamp, ensuring a solid electrical connection for the weld.
Keeping your welding needs organized not only speeds up the workflow but also prevents damage to expensive equipment. When your welding machine is secure on a cart, it is less likely to be knocked over or damaged by shop debris.
What Role Does Grounding Play in Safe Welding?
One of the most critical aspects of the welding operation is the electrical circuit. The current flows from the machine, through the torch, into the metal, and must return to the machine via the work clamp (ground clamp). If this connection is poor, the welding arc will be unstable, sputtering and sticking.
Worse, a bad ground can force the electricity to find other paths to return to the source—sometimes through sensitive electronics or even through the welder themselves. A high-quality ground clamp with a strong spring or screw mechanism is essential welding equipment. It should be attached directly to the clean metal of the workpiece, not to a rusty table leg or a painted surface.
Inspect your welding cables regularly. Cuts or frays in the insulation can lead to electric shocks or short circuits. Enhance safety by replacing damaged cables immediately.

Beyond the Basics: What Other Accessories Are Vital?
There are countless tools in welding that make life easier. Safety glasses are non-negotiable. Even when your helmet is up, you are likely grinding, chipping slag, or using a wire wheel. Debris flies everywhere. Wearing safety glasses under your welding helmet ensures that your eyes are protected when you flip the hood up to inspect your weld.
Magnets are another hero of the workshop. Magnetic squares hold pieces of metal at 45 or 90-degree angles, acting as a third hand while you tack weld parts together. Just remember to remove them before doing the final heavy weld, as the heat can demagnetize them.
Finally, consider the environment. If you are working on knees, knee pads are essential welding accessories. If you are working outside, wind shields are needed to protect the shielding gas. The list of essential welding tools and accessories grows with your experience, but starting with high-quality basics sets you up for success.
Key Takeaways for Every Welder
- Protect Your Eyes: Invest in a quality auto-darkening welding helmet to reduce neck strain and improve accuracy.
- Hand Safety is Paramount: Choose the right welding gloves for the task—thick cowhide for stick/MIG, thin goatskin for TIG.
- Dress for Sparks: Wear flame-resistant welding jackets or aprons. Avoid synthetic materials that melt.
- Breathe Clean Air: Use respirators or fume extraction systems to avoid long-term health issues.
- Secure Your Work: Use welding clamps, magnets, and a sturdy table to prevent warping and ensure geometric accuracy.
- Maintain Equipment: Check welding cables, electrode holders, and ground clamps daily for damage.
- Organize the Shop: Use welding carts and screens to keep the workspace efficient and safe for everyone.
- Inspect Consumables: Keep rods dry and wire clean to ensure every weld is strong and defect-free.
By investing in the right tools every welder needs, you not only improve the quality of your work but ensure that you can keep welding for years to come. Whether you are sourcing for a large distribution network or outfitting your own garage, quality gear is the best investment you can make.